Lectures for Information Technologies for Libraries and Information Agencies
Week 1 - Introduction | Social Software Tools | Multimedia Basics
Week 2 - Web Services | RSS, XML and Metadata
Week 3 - Internet and the World Wide Web (1)
Week 4 - Internet and the World Wide Web (2) | Web Services
Week 5 - Cascading Style Sheets (1)
Week 6 - Cascading Style Sheets (2) | Basic Web Design Principles | Testing & Debugging
Week 7 - Dynamic Web | Programming Concepts | Basics of Web Programming (1)
Week 8 - Forms in HTML | Basics of Web Programming (2)
Week 9 - Databases (1)
Week 10 - Databases (2) | Server Side Scripting (1)
Week 11 - Databases (3) | Server Side Scripting (2)
Week 12 - Recap of Key Concepts for Web Programming, Databases and Server Side Scripting
Week 13 - Evaluating Software Systems and Tools
Week 14 - How 550 connects to other MLIS courses
Week 15 - Course Review and Term Projects
View Page with Tabs | View Page without Tabs
Week 1 - Introduction | Social Software Tools | Multimedia Basics
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:48)
- Course Overview (9:25) Course Goals, Exercises, Project and Example, In a nutshell.
- Course Website (5:36) Gameplan, Schedule, Requirements, Exercises, Lectures: how best to search, LyndaCampus & Login.
- Software Tools (4:14) Google Accounts, Wiki - PBworks, Multimedia Resources.
- Multimedia Basics (2:36) Image formats.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex1 and throughout the course.
Demos
- Wiki
- PBwiki (1:15) How to create free wiki.
- Edit Class Wiki (4:50) How to create page and links.
- Web Design Fundamentals (LyndaCampus): Exploring Web Design, Getting Started, Web Terminology.
- How to Use Lynda.com (LyndaCampus)
- Web Design Fundamentals with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
|
Note: Content of this LyndaCampus course has changed in a major and the earlier videos mentioned in Lec 1 - Intro are not available anymore. |
Files
Download: Handout
Resources
- Google Account
- Wiki (PBworks)
- Multimedia Basics (Images, Audio, Video)
|
|
Google Account: Site | Wikipedia
|
- Wiki (collaboration)
|
Wiki in Plain English by Common Craft |
Wiki: Wikipedia | Tools: MediaWiki | PBworks Wikipedia is a Wiki: Wikipedia video by Common Craft
Wiki tool used in this class: PBworks
|
Multimedia Basics - Images | Audio | Video
|
Related
- Library & Information Technology
|
LITA Top Tech Trends Annual (2014 06/29/14) |
|
Week 2 - Web Services | RSS, XML and Metadata
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (5:36)
- Web Services 1 (1:46) Screencasting, Survey Tools.
- Web Services 2 (3:18) Google Drive, Google Spreadsheet, Screencast MediaRoll Widget).
- RSS (3:52) Feeds, Reader, Structure of RSS feed.
- XML & Metadata (10:25) Key Concepts.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex1 and throughout the class.
Demos
- Ex1 Demos
- Locate RSS Feed (3:43) How to find RSS Feed for website or blog and copy its RSS URL.
- Flickr + Pixlr (4:46) How to find images on flickr.com with a Creative Commons license and to use Pixlr to scale and crop images.
- Jing (4:28) How to use Jing to do screen capture and create screencasts and upload them to screencast.com.
- Google Spreadsheet (3:32) How to create a Google Spreasheet and set the sharing settings.
- Widgets (4:06) How to create Screencast widget and embed in a Wiki page.
- Screencast Embed Code (1:24) How to find embed code for a screencast.
- Google Drive Essential Training (LyndaCampus): Getting Started, Working with Files, Working with Spreadsheets, Collaborating with Google Docs.
- Google Drive Essential Training with Jess Stratton (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout
Resources
- Web Services (Screencasting, Survey Tools, Google Drive, Docs & Gadgets)
- RSS | XML | MetaData
Web Services - Screencasting | Surveys | Google Drive, Docs and Gadgets
|
|
|
|
|
Google Docs in Plain English by Common Craft |
Google Drive: Site | Wikipedia | Blog | Overview | Help
Google Docs: Site | Wikipedia | Overview | Help
Google Gadgets: Site | Wikipedia
|
- RSS = Real Simple Syndication to Pull Web and New content into One Place
|
RSS in Plain English by Common Craft |
RSS: Wikipedia | Digital Shift RSS
|
- XML = EXtensible Markup Language to pepresent data structures and documents
|
Why XML? by Sunlight Foundation Other Videos |
XML: Wikipedia Key Concepts
Tutorials |
- Metadata = Data about Data
|
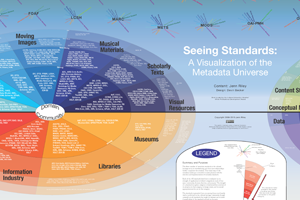
Metadata Universe Visualization by Jenn Riley at Indiana University provides overview of large number of metadata standards used in cultural heritage. |
Metadata: Wikipedia
Video for Fun: Oh Metadata! |
Related
|
|
World Wide Web: Wikipedia | Tim Berners-Lee | Web in Plain English
|
| Other videos by Michael Wesch |
Week 3 - Internet and the World Wide Web (1)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (5:33)
- HTML (13:14) Block and Inline Elements, Naming Elements, Hierarchy of Tags, Absolute vs. Relative Links.
- FTP & Permissions (10:39) Upload / Download Files, Permissions for Types of Users & Access.
- Demo Overview (7:10) Create & Upload Web Page.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex2-5 and the project site.
Demos
- HTML Demos
- Create Web Page (9:50) How to create a simple web page, using NotePad++, and how to preview the local page in the Browser.
- NetID and Eden Server account (4:36) Create / Check NetID, Activate Eden Server account, Create public_html folder if one does not already exists.
- Activate Your NetID & Eden Account: NetID/Password Activation and Service Activation.
- Upload Web Page (15:08) How to upload a web page to the public_html folder on the server, using Filezilla, set permissions, navigate to page in Browser, and refine site definition.
- Web Design Fundamentals (LyndaCampus): Exploring Web Design, Getting Started, Web Terminology.
- HTML Essential Training (LyndaCampus): Getting Started, Basic Page Structure, Formatting Page Content, Creating Links Controlling Styling.
- Web Design Fundamentals with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
|
Note: Content of this LyndaCampus course has changed in a major and the earlier videos mentioned in Lec 1 - Intro are not available anymore. |
- HTML Essential Training with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
Readings
Readings:
- Castro + Hyslop: Ch 1-4 (note: link attached to chapter number for examples provided for each chapter)
- Ch1: Web Page Building Blocks
- Ch3: Basic HTML Structure
- Ch4: Text
Resources
- HTML - HTML Resources, Basics, Doctype, Encoding, Validation, View Source Code.
- FTP - File Transfer Tools, File Permissions.
- HTML = HyperText Markup Language
|
|
- FTP = File Transfer Protocol and Permissions
|
|
Week 4 - Internet and the World Wide Web (2) | Web Services
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:26)
- HTML (15:06) Transition to HTML5, Key Rules, Doctype, Encoding, Tables, Links, Images.
- (optional) XHTML (17:15) Doctype, Encoding, Links, Tables, Images, Styles and key HTML5 differences.
- Ex2 Demo Overview (5:18)
- Ex2 - HTML5 (2:40) How to transition from XHTML to HTML5.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex2-5 and the project site.
Demos
- Exercise 2 Demos: Using XHTML or HTML5, Google Analytics.
- HTML Essential Training (LyndaCampus): Getting Started, Basic Page Structure, Formatting Page Content, Creating Links, Controlling Styling.
- Google Analytics Essential Training (LyndaCampus): What is Web Analytics, Fundamentals, Reports.
- Exercise 2 Demos XHTML and HTML5
|
XHTML
|
HTML5
|
|
|
- HTML Essential Training with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
- Google Analytics Essential Training with Brad Batesole (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
Readings
Readings:
- Castro + Hyslop: Ch 5, 6, 17, 18
- Ch5: Images
- Ch6: Links
- Ch17: Video, Audio, And Other Multimedia
- Ch18: Tables
Resources
- HTML (Doctype, Encoding, Links, Tables, Images, Styles)
- Google Analytics
|
- Google Analytics Measure Website Statistics and Effectiveness
|
More Videos: Google Analytics Channel on YouTube |
Google Analytics: Site | Wikipedia | Blog | Support
|
Week 5 - Cascading Style Sheets (1)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (3:54)
- HTML Elements (9:00) Hierarchy of Tags, Block and Inline Elements - div, id, class.
- HTML5 (7:56) Overview of key new features in HTML5.
- CSS (12:20) Why, What, Where, Location of CSS Style Definition, Structure of CSS Formatting Rule.
- CSS3 (2:38) Overview of key new features in CSS3.
- CSS Demo Overview (2:00)
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex3-5 and in project site.
Demos
- CSS Demo - XHTML (14:28) Create hierarchy of DIVs and assigin IDs; Specify CSS in the head of web page; Explore CSS Reference; Comment out code to see effect of specific CSS code.
- CSS Demo - HTML5 (5:48) Show how to convert XHTML and/or DIVs into HTML5 tags and update related CSS rules.
- CSS Fundamentals (LyndaCampus): CSS Basics, Common CSS Concepts, CSS Resources.
- HTML5: Structure, Syntax, and Semantics (LyndaCampus): Basics, Structure, Grouping Content.
- CSS Fundamentals with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
|
|
- HTML5: Structure, Syntax, and Semantics with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
Readings
Readings:
- Castro + Hyslop: Ch 7, 8, 10
- Ch7: CSS Building Blocks
- Ch8: Working with Style Sheets
- Ch10: Formatting Text with Styles
Resources
- HTML Elements Recap (Hierarchy of Tags, Block and Inline Elements - div, id, class)
- Cascading Style Sheet (Why, What, Where, Location of CSS Style Definition, Structure of CSS Formatting Rule)
- HTML5 & CSS3
|
- CSS = Cascading Style Sheet
|
|
|
|
Week 6 - Cascading Style Sheets (2) | Basic Web Design Principles | Testing & Debugging
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:18)
- CSS Cascade (17:40) Inheritance, Specificity & Location Cascade, Constructing Complex Selectors.
- Box Model (4:08) Box Model: width, height, padding, border, margin, box-sizing, overflow.
- Floating & Positioning Elements (7:22) Floating Element, Absolutely Positioned Element, CSS properties: float, clear, position, display.
- CSS Reset (2:26) "Clean Slate" CSS, Make HTML5 Backwards Compatible, HTML5 shiv.
- Ex3 & Demo Overview (9:22) Ex3 Overview, Ex3 Demo Steps Overview.
- Web Design Principles (3:44)
- Test & Debug (5:45) Easy Things to Check First.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex3-5 and in project site.
Demos
- Exercise 3 Demo
- Step 1 (6:35) Download files, Link to External CSS file; Comment out CSS "Clean Slate" code.
- Step 2 (2:00) Create DIVs to control presentation.
- Step 3 (1:00) Create HTML5 to describe semantics.
- Step 4 (4:40) Add Floating Sidebar, Create <aside> element.
- Step 5 (9:14) Ensure footer has nothing floating to its left and right; Add Floating Image in main content.
- Step 6 (8:16) Embed YouTube Video / Screencast; Next Steps.
- CSS: Page Layouts (LyndaCampus): Design Considerations, Layout Basics, Floats, Positioning Elements, Create Fixed / Flexible / Responsive Layouts.
- CSS: Page Layouts with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
- CSS: Page Layouts: Exercise Files and video: Using Exercise Files
Readings
Readings:
- Castro + Hyslop: Ch 9, 11, 15, 20
- Ch9: Defining Selectors
- Ch11: Layout with Styles
- Ch15: Lists
- Ch20: Testing and Debugging Web Pages
- Knight Digital Media Center
- CSS (Recap)
- Web Design Templates
- Embed Media (optional)
- Embed Widget (optional)
Resources
- CSS - Inheritance, Specificity & Location Cascade, Constructing Complex Selectors, Box Model, Floating Element, Absolutely Positioned Element.
- Basic Web Design Principles
- Test & Debug Web Pages - Check Easy Things First.
|
Slideshare presentation by Amit Tyagi |
|
|
|
Related
|
Week 7 - Dynamic Web | Programming Concepts | Basics of Web Programming (1)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (5:14)
- Dynamic Web (5:50) JavaScript, PHP, MySQL, Apache.
- Programming (7:20) Basic Programming Concepts.
- JavaScript (22:25) Basic Elements, Document Object Model, Image Rollovers.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex4, Ex5 and the project site.
Demos
- JavaScript Demos
- Hello World (4:48) Change Text and apply h2 tag; Add "+ Date()" to text being displayed; Add paragraph before and after where JavaScript is inserted
- Detect Visitor's Browser: Examine JavaScript code to detect visitor's browser and display this information in the web page - part of JavaScript narrated lecture.
- Image Rollover: how to create an image rollover effect using JavaScript - part of JavaScript narrated lecture.
- JavaScript Essential Training (LyndaCampus): Syntax, DOM, UI, Best Practices, Libraries, HTML5.
- JavaScript Essential Training with Simon Allardice (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
- JavaScript Essential Training: Exercise Files and video: Using Exercise Files
Readings
Readings:
Resources
- Dynamic Web - JavaScript, PHP, MySQL, Apache.
- Basic Programming Principles
- JavaScript - Basic Elements, Document Object Model
|
|
- JavaScript Client-side scripting language
|
Related
Slideshows:
- MCIS 507 Lecture: Image Slideshows (9:15) HTML & CSS Properties, jQuery, Slideshows: Galleria, Galleriffic, Supersized.
- Demos (using NotePad++):
- Galleria Slideshow | demo
- Customizing Galleria (8:40) What to customize.
- Beginner's Guide
- Galleriffic Slideshow | demo
- Customizing Galleriffic (8:44) What to customize.
- Supersized Slideshow | demo
- Customizing Supersized (6:34) What to customize.
Week 8 - Forms in HTML | Basics of Web Programming (2)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:10)
- Forms in HTML (12:18)
- Forms in HTML5 (3:33)
- JavaScript to Validate Form (24:20).
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex4 and the project site.
Demos
- Ex4 Demo
- Ex4 Demo - Overview (10:38) reviewing key aspects of Ex4 and what the key challenges are.
- Ex4 Demo - Next Step 1 (5:05) Key validation tasks; Customize function to test that at least two checkboxes are selected.
- Ex4 Demo - Next Step 2 (6:18) Create function to test that State field has two characters.
- Ex4 Demo - Next Step 3 (6:58) Customize form; Remove field; Change field name & troubleshoot; Customize radio buttons.
- HTML Essential Training (LyndaCampus): Basic Scripting.
- HTML Essential Training with James Williamson (LyndaCampus)
|
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
Readings
Readings:
- Castro v6: Ch 17
- Ch17 chapter: Forms
- Castro + Hyslop: Ch 16, 19
- Ch16: Forms
- Ch19: Adding JavaScript
- Nixon: Preface and Ch 1, 11, 14
- Preface
- Ch1: Introduction to Dynamic Web Content
- Ch11: Form Handling (complements what is covered in class)
- Ch14: Exploring JavaScript (complements what is covered in class)
Resources
- Forms in HTML
- JavaScript - Form Validation
- Forms in HTML Collect data from page visitors
|
- JavaScript Client-side scripting language
|
JavaScriptTeacher Videos: Basics (shown above) | Variables | Input | Functions |
Week 9 - Databases (1)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:28)
- Relational Database (19:24) Key Relational Database concepts.
- studentweb Server (2:48) How to create studentweb account; How to navigate to course folder on studentweb server.
- MySQL Credentials (2:04) MySQL Username & Password.
- MySQL Workbench (2:04) Install MySQL Workbench; Create Connection.
- SQL Demo Overview (3:39) Specify database, Create table, Run queries.
- MySQL Workbench and SFTP (0:39) Recap of MySQL Workbench and SFTP settings.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex5 and the project site.
Demos
- MySQL Demos
- Studentweb Server & MySQL Password (5:32) How to create New Site in Filezilla to connect to studentweb server and locate "mysqlpassword.txt" file that contains the password for your MySQL database.
- MySQL Workbench v6(2:05) How to create new connection or edit it and watch MySQL Workbench (12:56) How to create a new connection and then connect to your MySQL database on "studentweb" server; make sure Preferences are set correctly; how to create a table and add data; how to query a table.
- Edit Table Data (1:52) How to delete row(s) from table in your MySQL database using MySQL Workbench.
- Foundations of Programming: Databases with Simon Allardice (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
Readings
Readings:
- Nixon:
-
Ch8: Introduction to MySQL (read 8.1, 8.2, 8.4.2 ; scan: 8.3.3, 8.3.4)
Resources
- MySQL Open-Source Relational Database and SQL = Structured Query Language
|
|
Week 10 - Databases (2) & Server Side Scripting (1)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (4:22)
- PHP 1 (8:46) Introduction to PHP.
- PHP 2 (19:58) Variable Naming Rules, Strings, Arrays, Operators, IF test, FOR loop.
- studentweb Server (2:10) Using Filezilla to connect to studentWeb server and course folder.
- PHP & MySQL (13:10) Using PHP to connect to MySQL database and extract data.
- Credentials Management (1:18) Username and password credentials to use in MySQL Workbench, SFTP, PHP.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex5 and the project site.
Demos
- PHP Demos
- Download PHP step-by-step files (3:12) How to download PHP step-by-step files for Weeks 10 and 11 by selecting .txt file and then saving it as a .php to the local computer.
- Customize Filezilla (2:16) so that you are directly dropped into the folder with your username in the YourCourseFolder on the studentweb server.
- login_yourname.php (4:36) How to specify MySQL username & password in PHP file; Upload to server and set permissions; Test in Browser and View Source to notice that the PHP code is not visible.
- Step 1 (4:36) require_once; Interpret error message; mysql_connect; mysql_select_db.
- Step 2 (3:14) Formulate SQL query, send to MySQL database and receive result table; Introduce intentional spelling mistake to practice how to troubleshoot; Test file in Browser.
- Step 3 (3:52) Use FOR loop to display result table; Use MySQL Workbench to make sure correct field names are used.
- Step 4: (4:16) Use mysql_fetch_row to make code more efficient; Use MySQL Workbench to determine the correct numercial index for specific fields in result table.
- PHP with MySQL Essential Training (LyndaCampus): First Steps, Data Types, Control Structures, Functions, Debugging, Web Pages, MySQL Basics.
- PHP with MySQL Essential Training with Kevin Skoglund (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
LyndaCampus:
- PHP with MySQL Essential Training: Exercise Files and video: Using Exercise Files
Readings
Readings:
- Nixon: Ch 3-6 and 10
- Ch3: Introduction to PHP
- Ch4: Expressions and Control Flow in PHP (read up to and including 4.4.4.)
- Ch5: PHP Functions and Objects (read up to and including 5.3.)
- Ch6: PHP Arrays (read up to and including 6.2.; remaining sections are there for reference)
- Ch10: Accessing MySQL Using PHP
- 10.1: how to access & display data in MySQL database using PHP.
- 10.2: how to add & delete data form MySQL database using a form and PHP.
- 10.3: practical example that we will try to emulate in part.
Resources
- PHP Server-side scripting language
|
|
Week 11 - Databases (3) & Server Side Scripting (2)
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (7:12)
- Credentials Management Recap (3:09) Recap of username and password credentials to use in MySQL Workbench, SFTP, PHP; URL to use to access studentweb pages.
- PHP & MySQL Recap (6:20) Recap of steps needed to use PHP to connect to MySQL database and extract data, Overview of Ex5 steps and steps covered in Week 10.
- Ex5 Demo Overview (18:38)
- Ex5 Form Using HTML5 (1:20) How to use HTML5 Form Validation in Form with radio buttons.
Exercises: content covered will be used in Ex5 and the project site.
Demos
- Exercise 5 Demo
- Download PHP step-by-step files (3:12) How to download PHP step-by-step files for Weeks 10 and 11 by selecting .txt file and then saving it as a .php to the local computer.
- Customize Filezilla (2:16) so that you are directly dropped into the folder with your username in the YourCourseFolder on the studentweb server.
- login_yourname.php (4:36) How to specify MySQL username & password in PHP file; Upload to server and set permissions; Test in Browser and View Source to notice that the PHP code is not visible.
- Steps 1-4 covered in Week 10 Demos.
- Step 5 (1:48) Discuss form with radio buttons and JavaScript validation functions and how to extend to be able to collect feedback for 10 tools.
- Step5_HTML5 (3:37) Convert to XHTML Step 5 page to HTML5 and how to use HTML5 Form validation.
- Step 6 (2:46) Discuss PHP code to display $_POST and the displayPostArray function.
- Step 7 (7:48) Create "tools" table in MySQL database using MySQL Workbench; discuss how to extend CREATE TABLE query
- Step 8 (5:54) Discuss PHP code needed to connect to MySQL database; Use isset function to make sure values in $_POST are defined; Cleanse data using mysql_fix_string function; Create SQL query to insert form data in "tools" table in MySQL database; Use MySQL Workbench to check that data got inserted into "tools" table.
- Step 9 (1:20) Discuss PHP code needed to display contents of "tools" MySQL table.
- Step 10 (5:35) Discuss how to incorporate CSS & HTML in PHP code; Show how to compute up-to-date average score for each tool by using SQL query that returns sum of scores for each tool; Show how to comment out code; Test PHP page on server.
- Step 10 HTML5 (5:00) Convert Step10 form and showResults pages to HTML5 and use HTML5 Form validation; Test in browser and use MySQL Workbench to test what is written into "tools" table.
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
Readings
Readings:
- Nixon: Ch 17 and Appendix B & D
- Ch17: JavaScript and PHP Validation and Error Handling
Contains JavaScript validation functions used (in part) in Exercises 4 & 5 and shows how to include them in PHP code. - Appendix B: Online Resources
- Appendix D: MySQL Functions
Resources
- MySQL, PHP and CSS Dynamically Created Web Pages
|
|
Week 12 - Recap of Key Concepts for Web Programming, Databases and Server Side Scripting
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (2:10)
- Recap of Key Concepts for Web Programming, JavaScript, MySQL & PHP
- HTML (15:06) Transition to HTML5, Key Rules, Doctype, Encoding, Tables, Links, Images.
- HTML Elements (9:00) Hierarchy of Tags, Block and Inline Elements - div, id, class.
- CSS (12:20) Why, What, Where, Location of CSS Style Definition, Structure of CSS Formatting Rule.
- CSS Cascade (17:40) Inheritance, Specificity & Location Cascade, Constructing Complex Selectors.
- Box Model (4:08) Box Model: width, height, padding, border, margin, box-sizing, overflow.
- Floating & Positioning Elements (7:22) Floating Element, Absolutely Positioned Element, CSS properties: float, clear, position, display.
- CSS Reset (2:26) "Clean Slate" CSS, Make HTML5 Backwards Compatible, HTML5 shiv.
- JavaScript (22:25) Basic Elements, Document Object Model, Image Rollovers.
- PHP (19:58) Variable Naming Rules, Strings, Arrays, Operators, IF test, FOR loop.
- Credentials Management Recap (3:09) Recap of username and password credentials to use in MySQL Workbench, SFTP, PHP; URL to use to access studentweb pages.
- PHP & MySQL Recap (6:20) Recap of steps needed to use PHP to connect to MySQL database and extract data, Overview of Ex5 steps and steps covered in Week 10.
- Test & Debug (5:45) Easy Things to Check First.
Demos
- Project Demo
- Step 0 (1:02) Collect needed Ex3, Ex4 and Ex5 pages and external CSS files, images etc.
- Step 1 (4:54) Use Ex3 pages as starting point; Create Primary Navigation: Home | Info Tech | Interest | About.
- Step 2 (2:58) Create Info Tech - Intro, Interests - Intro and About pages.
- Step 3a (2:54) Info Tech page: Create Secondary Navigation.
- Step 3b (8:45) Create Info Tech page: Open-Source tool + Validated Form = Ex4; Disable HTML5 built-in validation and use JavaScript.
- Step 3c (8:15) Create Info Tech pages: InfoTech + Form to PHP and PHP Results = Ex5.
- Step 4 (2:38) Create "you are here" indicator for Info Tech - Results page.
- Step 5 (4:56) Upload Project and Test in Browser.
Files
Download: Handout | Step-by-Step
Week 13 - Evaluating Software Systems and Tools
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (3:55)
- Working on Exercises and Project.
- Optional Demos: Open-source Blogging and Content Management Systems (CMS).
Demos
Optional:
- Wordpress Essential Training: open-source Blogging and Content Management System used by almost 20% of top 10M websites.
- Joomla! 3 Essential Training: open-source Content Management System and second most used CMS after WordPress.
- Drupal 7 Essential Training: open-source Content Management System and used in over quarter million web sites.
- WordPress 3.x Tutorials | WordPress Essential Training with Morten Rand-Hendriksen (LyndaCampus)
- Joomla! 3 Essential Training with Jen Kramer (LyndaCampus)
- Drupal 7 Essential Training with Tom Geller (LyndaCampus)
Files
Download: Handout
LyndaCampus:
- Joomla! 3 Essential Training: Exercise Files and video: Using Exercise Files
- Drupal 7 Essential Training: Exercise Files and video: Using Exercise Files
Resources
|
Tim O’Reilly's "Open Source and Open Data in the Age of the Cloud" presentation on SlideShare.
|
|
Week 14 - How 550 connects to other MLIS courses
Lectures
Topics:
- Intro (1:40)
- MLIS Courses (15:30) Digital Libraries courses, Metadata, Databases, Information Retrieval, Multimedia Production,
Information Visualization, Interface Design. - Working on Exercises and Project.
Files
Download: Handout